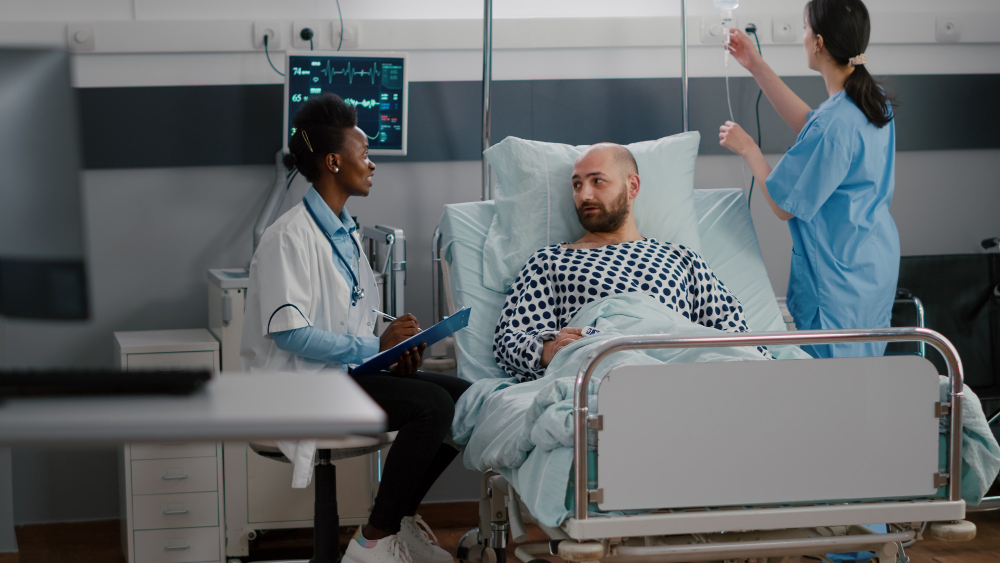
It may be challenging to know precisely what to give a patient with hypertension since there are so many various kinds of IV fluids available to meet varied patient demands and the best center is IV fluids treatment Watauga, mainly if there are additional illnesses to take into account. It is crucial to comprehend what hypertension is, how it affects the body chemically, and the chemical processes the body utilizes to combat it to thoroughly understand your choices while treating hypertensive patients with IV fluids.
When the oral route cannot be utilized, intravenous fluids, sometimes referred to as intravenous solutions, are used as extra fluids in intravenous treatment to restore or maintain average fluid volume and electrolyte balance. Mono Lab test Watauga is a quick and easy center for infusing drugs, blood products, and fluids directly into the intravascular fluid compartment while restoring electrolyte deficits.
Various IV Fluid Types
IV fluids may be categorized in various ways and according to different IV fluid kinds.
Based on their Tonicity, IV Fluids are often categorized:
- Isotonic.
- Hypotonic
- Hypertonic
The Function of IV Solutions may also be used to classify them:
After a significant loss of plasma or blood, solutions are employed to increase blood volume. In essence, hypertension is elevated blood pressure. Several variables might contribute to this high blood pressure.
Through a variety of physiological processes, your body fights hypertension. One of three basic mechanisms by which the brain’s cardiac center may control heart rate is as follows:
- The heartbeat, the amount of blood flowing through the arteries, and the heartbeat
- Lowering heart rate, reducing blood flow via the arteries, and reducing cardiac output
- Causing the vasomotor center to start vasodilation, which narrows or widens the arteries by forcing them to contract or relax
The body employs several processes, including the heart, to raise blood pressure. Using different hormones is critical for the body to control blood pressure without altering heart rate.
Renin is released into the blood by the kidneys from the juxtaglomerular cells. Angiotensin II works in two ways to control blood pressure:
It causes the kidneys’ blood arteries to tighten, raising renal blood pressure and decreasing blood flow to the kidneys.
Because the blood flows through the kidneys, less blood is filtered by them, which results in more blood volume and water in the blood, which raises blood pressure.
Applications in Practice
Now that you know a little about how the body controls blood pressure, it’s time to put that knowledge to use and determine which IV fluids may be administered to individuals with hypertension.
Avoid utilizing regular or salt-based saline solutions if a patient has hypertension and you cannot identify the cause. The salts in a standard saline solution may exacerbate hypertension if a person already has high blood pressure due to other factors, particularly if that person has a high sodium concentration in their blood, increasing blood volume and making the body work harder to control their hypertension.
Standard saline solutions, however, are helpful if someone has hypertension brought on by blood sugar levels from food or illnesses like diabetes. A typical saline solution is made with the same amount of salt the body naturally contains.
There is no simple answer as to what universal IV fluids should be used on people with hypertension since the medicine may be a highly complicated science with many variables at play. Depending on the patient, hypertension may not be an issue since the other diseases are more severe or are working to reduce or eliminate hypertension (such as increasing body fluid due to severe dehydration or blood loss). When giving IV fluids, treat each patient individually since other factors than hypertension might affect the optimal course of action. As they are the most familiar with your medical history, contact your doctor if you have any questions regarding which IV fluid therapies would be the best for you, if you even need them.
What are this Procedure’s Benefits and Risks?
If you are significantly unwell, IV rehydration is a standard, easy, and safe therapy that may help you feel better immediately and save your life.
However, uncommon issues might arise, such as:
Collapsed Vein: When a needle or an IV is in place for a long time, the vein may sometimes collapse.
Fluid Overload: Headaches, high blood pressure, and breathing difficulties might occur if you get too much fluid too rapidly. Fluid levels may generally be adjusted to address this rapidly. However, it could be harmful.
Infection: An infection might happen if the region is not transparent when the needle is put. In most cases, antibiotics are used by your healthcare professional to treat infections.
Infiltration: Fluids may infiltrate the tissues around the vein if the needle moves or becomes dislodged.
Phlebitis: When the vein swells due to the IV, phlebitis ensues. One of the more frequent problems, but one that is often quickly resolved by taking out the IV in minuteclinic strep test Watauga, using a warm compress, and elevating the arm.